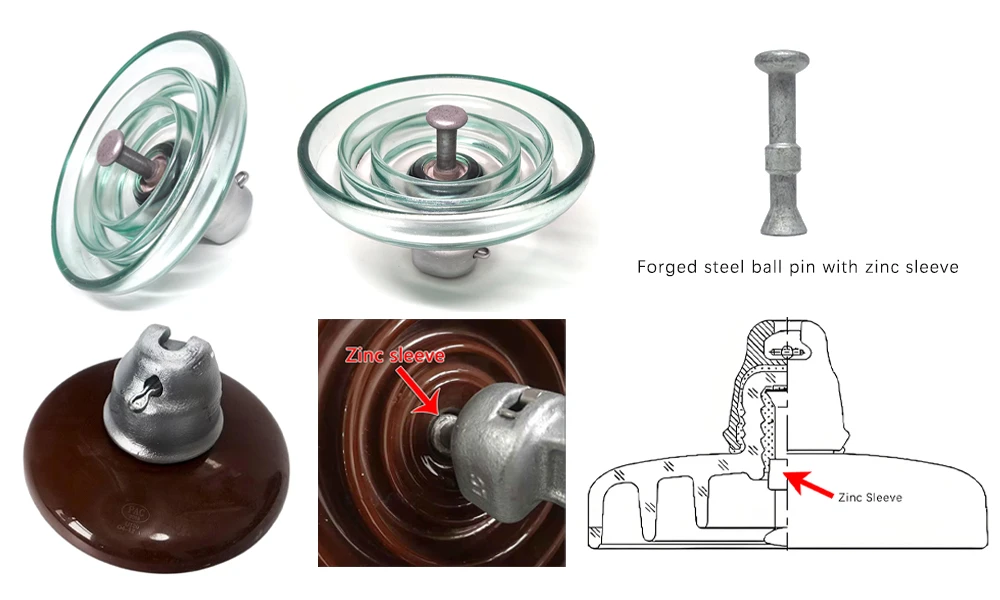
Les isolateurs à manchon en zinc sont des isolateurs standards équipés d’un manchon en zinc pour améliorer la résistance à la corrosion. Ils sont couramment utilisés dans les lignes de transmission et de distribution haute tension, notamment pour les applications en ultra-haute tension au-delà de 500 kV ou dans des conditions environnementales sévères.
Le zinc possède un potentiel électrochimique plus faible que l’acier forgé, ce qui signifie qu’il se corrode en premier, protégeant ainsi la broche en acier contre la rouille et l’affaiblissement. Même lorsque le manchon en zinc s’oxyde progressivement, cela n’affecte pas la résistance mécanique de l’isolateur. Cela garantit des performances durables à long terme dans des environnements extérieurs difficiles.
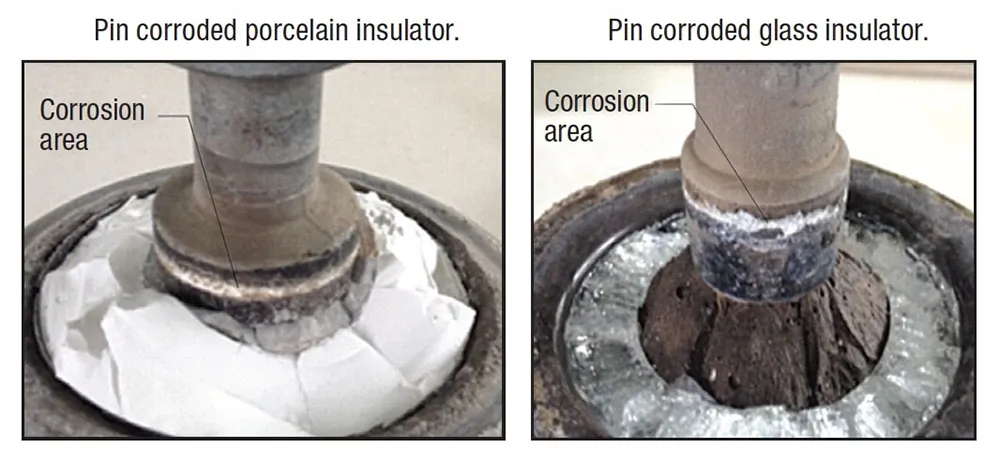
La source de l’image : INMR.com
Quand utiliser les isolateurs à manchon en zinc ?
| Scénario d’application | Recommandation |
| Zones propres ou urbaines | ❌ En général, non nécessaire |
| Zones fortement polluées (côtières, industrielles, désertiques) | ✅ Optionnel, mais pas obligatoire |
| Environnements très humides, pluies acides ou chargés en sel | ✅ Recommandé pour une meilleure protection |
| Régions de haute altitude (sujettes aux décharges corona) | ✅ À considérer si besoin |
Structure de l’isolateur à manchon en zinc
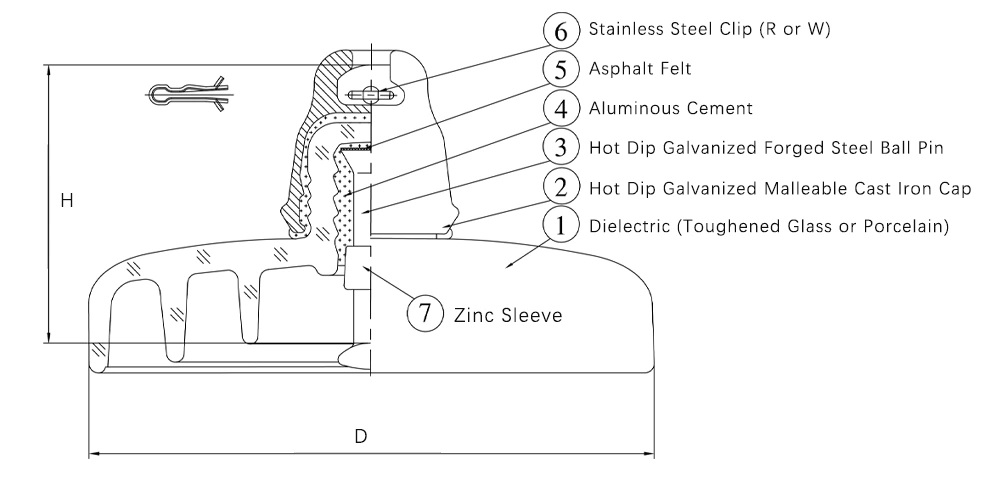
1. Diélectrique (verre trempé ou porcelaine)
2. Capuchon en fonte malléable galvanisée à chaud
3. Broche sphérique en acier forgé galvanisé à chaud
4. Ciment aluminique
5. Feutre bitumé
6. Agrafe en acier inoxydable (type R ou W)
7. Manchon en zinc