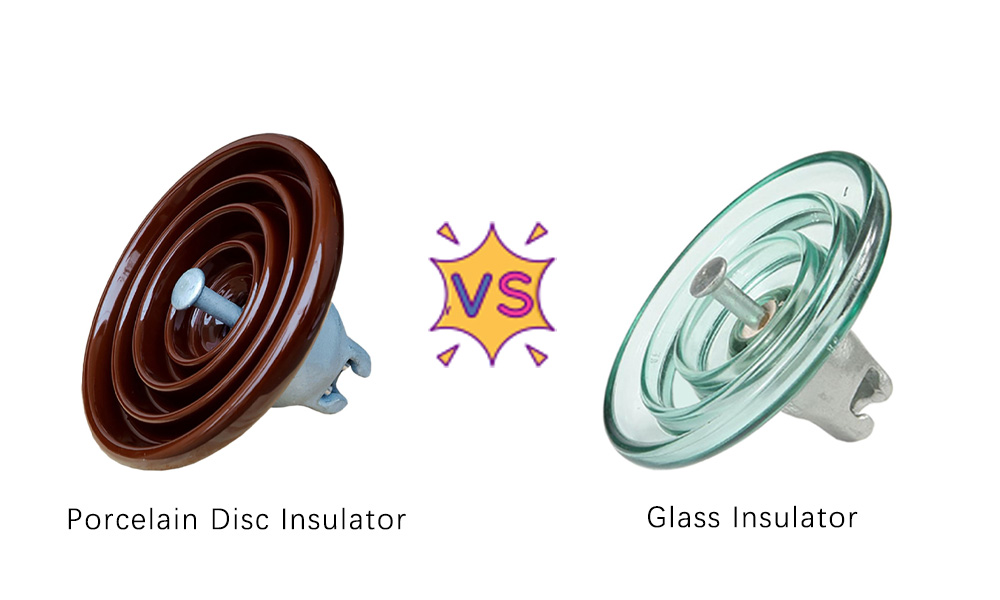
Los aisladores de suspensión de porcelana y los aisladores de vidrio se utilizan ampliamente en los sistemas de transmisión y distribución de energía eléctrica en alta tensión. Su función principal es proporcionar soporte mecánico a los conductores y aislarlos eléctricamente de las torres de transmisión.
Aunque ambos cumplen eficazmente esta función, existen diferencias importantes en cuanto a materiales, rendimiento y aplicación.
Materiales de fabricación
- Aisladores de suspensión de porcelana: Están fabricados con porcelana eléctrica de alta resistencia (normalmente porcelana de alúmina) y recubiertos con un esmalte vidriado para mejorar el aislamiento y la resistencia a la contaminación.
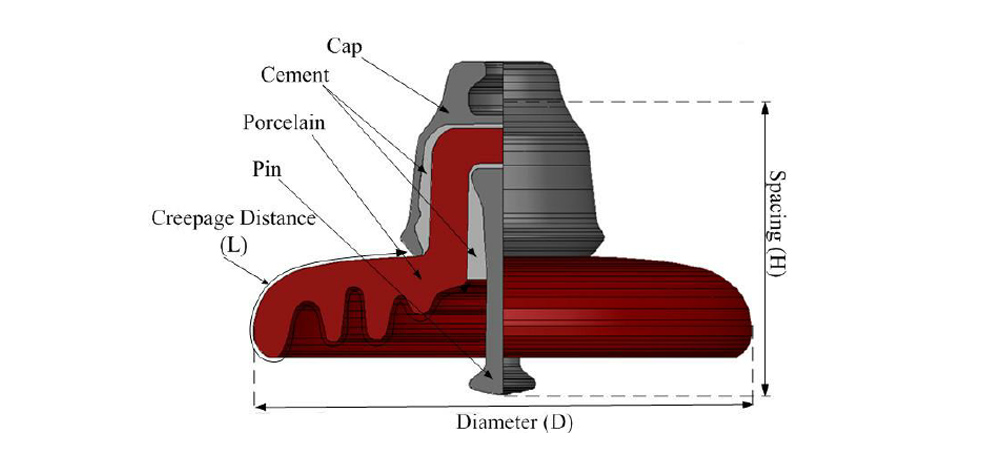
- Aisladores de vidrio: Están hechos de vidrio templado, sometido a un proceso de templado térmico que incrementa significativamente su resistencia mecánica.
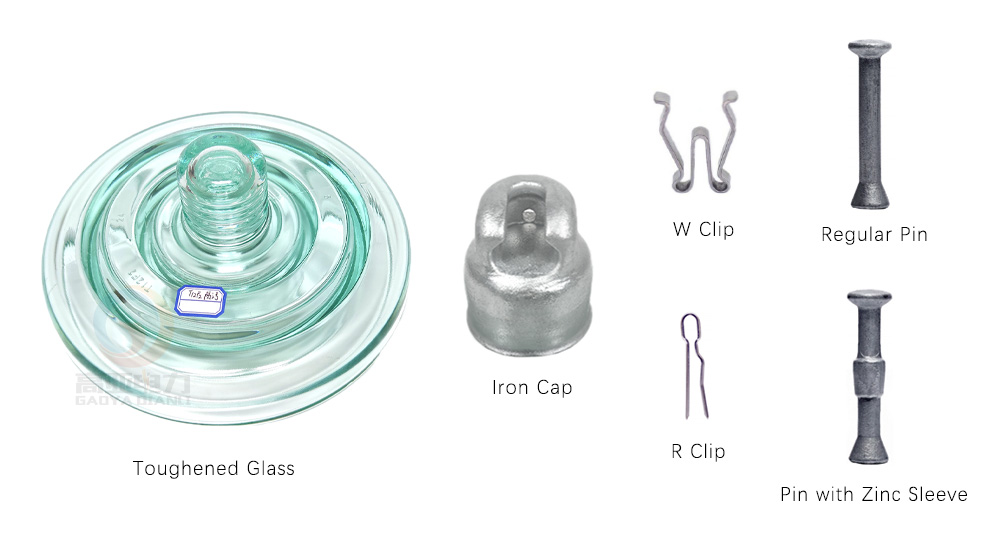
Propiedades mecánicas y eléctricas
| Desempeño | Aisladores de suspensión de porcelana | Aisladores de vidrio |
| Resistencia mecánica | Alta resistencia, buena tracción, pero susceptibles a fisuras | Más frágiles al impacto externo, aunque el vidrio templado tiene mayor resistencia |
| Resistencia a impactos | Pueden desarrollar microgrietas y envejecen con el tiempo | Superficie lisa, excelente resistencia a impactos |
| Aislamiento eléctrico | Afectado por la humedad y la contaminación | Aislamiento más estable y menos sensible a condiciones ambientales |
| Resistencia al envejecimiento | Su rendimiento puede disminuir con el tiempo debido a la corrosión o variaciones térmicas | Tienen función autodiagnóstica: si fallan, se rompen visiblemente para fácil detección |
Operación y mantenimiento
Aisladores de suspensión de porcelana:
- Son propensos a desarrollar grietas internas difíciles de detectar, lo cual requiere inspecciones frecuentes.
- Su desempeño se ve más afectado por la humedad y la contaminación, lo que acelera el envejecimiento del material.
Aisladores de vidrio:
- Poseen una propiedad autodestructiva: si hay un daño estructural, el aislador se rompe, lo que permite identificar y sustituir fácilmente unidades defectuosas.
- Su vida útil es más larga y son menos sensibles a las condiciones ambientales. Incluso después de 30 o 40 años, mantienen su rendimiento eléctrico y resistencia mecánica.
Ambientes de aplicación
- Aisladores de suspensión de porcelana: Adecuados para una variedad de condiciones climáticas, pero en ambientes altamente contaminados o húmedos pueden requerir medidas adicionales contra la contaminación.
- Aisladores de vidrio: Gracias a su superficie lisa, resisten mejor la acumulación de suciedad, siendo ideales para zonas costeras, industriales o con alta humedad ambiental.
Consideraciones económicas
- Los aisladores de vidrio suelen ser más rentables debido a su proceso de fabricación estandarizado y al menor coste de los materiales.
- Los aisladores de suspensión de porcelana pueden tener un coste total más elevado, tanto por la complejidad del proceso de fabricación como por los mayores requerimientos de mantenimiento.

