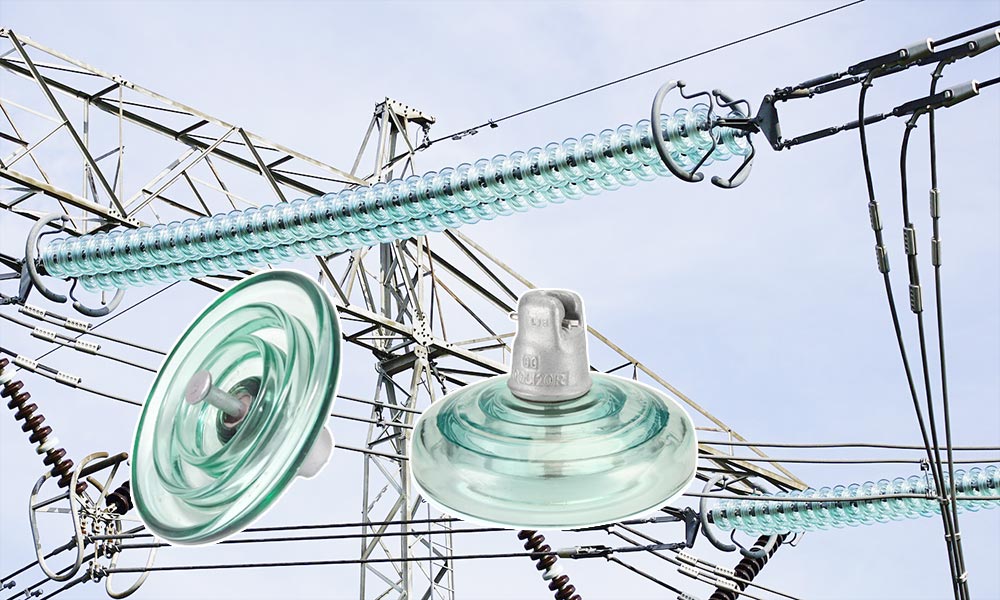
Un aislador de vidrio para alta tensión, también conocido como aislador de vidrio templado, es un componente de aislamiento eléctrico utilizado en líneas de transmisión y distribución de alta tensión. Generalmente se ensambla en cadenas de aisladores para soportar los conductores y evitar fugas de corriente. Fabricado por primera vez en la década de 1950, este tipo de aislador se ha utilizado ampliamente desde entonces debido a su excelente resistencia mecánica y rendimiento eléctrico.
¿cómo se fabrican los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión?
El aislador de vidrio para alta tensión está compuesto por un disco de vidrio templado, una tapa y espiga galvanizadas en caliente, y un clip de seguridad de acero inoxidable, todos unidos con un adhesivo de cemento de alta resistencia.
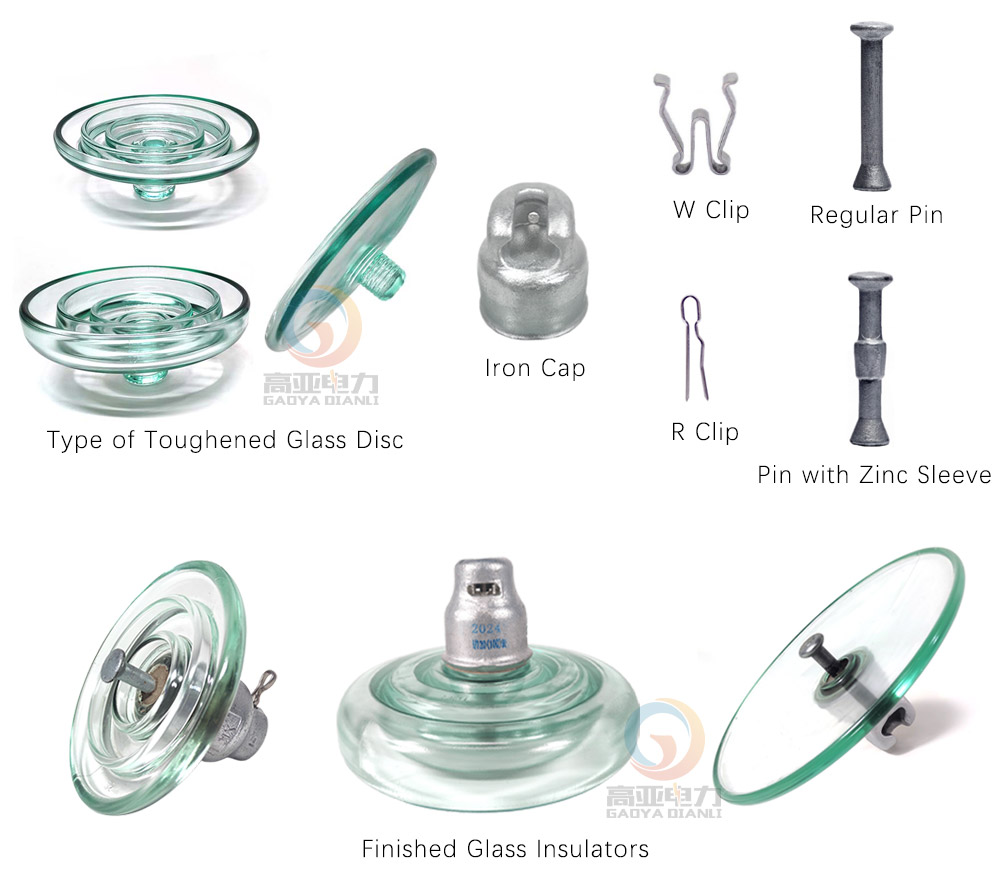

Proceso de fabricación de aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión (cómo se hace el disco de vidrio templado):
1. Preparación de materias primas - 2. Fusión - 3. Moldeo - 4. Recocido - 5. Templado - 6. Inspección de calidad - 7. Almacenamiento y transporte
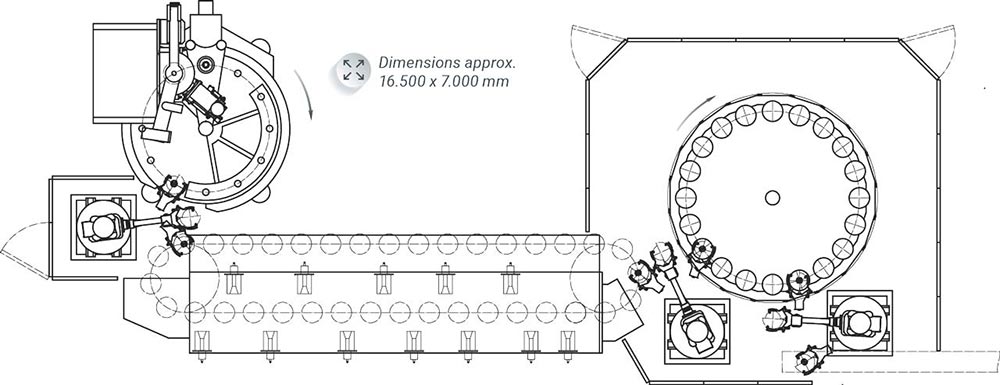
Diagrama de la línea de producción de aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión
¿cómo funcionan los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión?
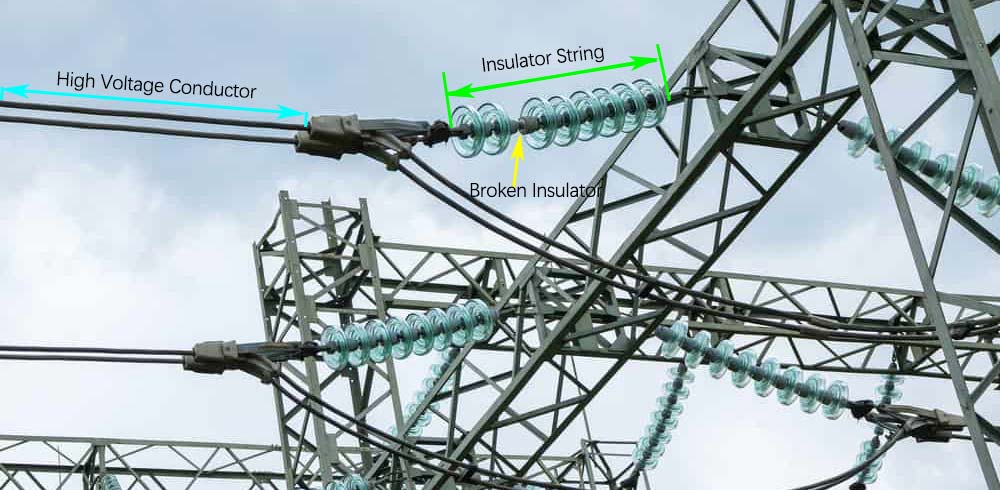
Soporte mecánico
Los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión soportan esfuerzos mecánicos como tensión, viento y carga de hielo gracias a:
- Vidrio templado: Mejora la durabilidad y garantiza la estabilidad de la línea.
- Configuración en serie: Múltiples aisladores en una cadena se adaptan a distintos niveles de voltaje y carga.
- Función autodestructiva: Si el aislador se rompe, el vidrio se fragmenta de forma segura mientras las piezas metálicas permanecen conectadas, evitando fallos del sistema.
Aislamiento eléctrico
Estos aisladores evitan que la corriente de los conductores de alta tensión se derive hacia las torres o postes conectados a tierra mediante:
- Material de alta resistencia: El vidrio es un mal conductor, lo que bloquea eficazmente el paso de la corriente.
- Distancia de fuga extendida: Diseños tipo disco u abiertos aumentan la distancia superficial, reduciendo el riesgo de descargas superficiales.
- Propiedades antipolvo: La superficie lisa del vidrio resiste la acumulación de suciedad, lo que minimiza el riesgo de fallos eléctricos.
cómo elegir los aisladores de vidrio adecuados para alta tensión: 3 factores clave
1. Planos y parámetros técnicos
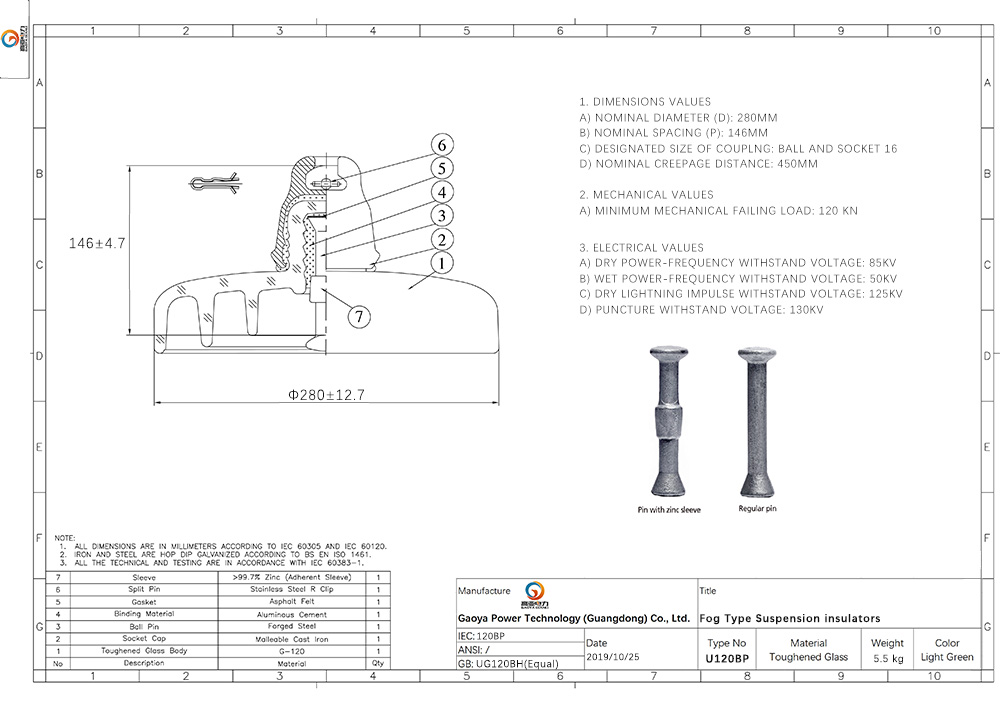
Al elegir aisladores de vidrio, se deben tener en cuenta los siguientes parámetros técnicos:
- Distancia de fuga nominal: Cuanto mayor sea, menor es el riesgo de descarga por contaminación.
- Carga mínima de rotura mecánica: Por ejemplo, 120 kN (según el dibujo técnico).
- Tamaño de acoplamiento: Un tamaño estandarizado facilita el ensamblaje de la cadena.
- Accesorios galvanizados en caliente: Mayor resistencia a la corrosión y mayor durabilidad.
Puede optar por normas internacionales IEC o ANSI según los requisitos de su proyecto. Para realizar un pedido, basta con proporcionar los planos y especificaciones técnicas al fabricante para que verifique y cotice en base a sus necesidades.
2. Selección según el voltaje de línea
La elección del aislador de vidrio para alta tensión adecuado debe basarse en el voltaje de la línea. Puede consultar la siguiente tabla como referencia.
| Tipos y modelos de aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión | Nivel de tensión (kV) | |
| Aislador de vidrio de perfil estándar | U40B(CTV175) | 10kV-66kV |
| U70BS | 10kV-330kV | |
| U70BL | 10kV-330kV | |
| U120B | 10kV-330kV | |
| U100BS | 10kV-330kV | |
| U100BL | 10kV-330kV | |
| U120B | 10kV-330kV | |
| U160BS | 10kV-500kV | |
| U160BM | 10kV-500kV | |
| U160BL | 10kV-500kV | |
| U210B | 10kV-500kV | |
| U240B | 10kV-500kV | |
| U300B | 10kV-500kV | |
| U420B | 10kV-500kV | |
| U530B | 10kV-1000kV | |
| U550B | 10kV-1000kV | |
| Aislador de vidrio de perfil antipolución | U70BLP | 10kV-330kV |
| U100BP | 10kV-330kV | |
| U100BLP | 10kV-330kV | |
| U120BP | 10kV-330kV | |
| U160BP | 10kV-500kV | |
| U210BP | 10kV-500kV | |
| U240BP | 10kV-500kV | |
| U300BP | 10kV-500kV | |
| Aislador de vidrio de perfil aerodinámico | U70BSM | 10kV-330kV |
| U70BLM | 10kV-330kV | |
| U100BSM | 10kV-330kV | |
| U100BLM | 10kV-330kV | |
| U120BLM | 10kV-330kV | |
| U160BSM | 10kV-500kV | |
| U160BMM | 10kV-500kV | |
| U160BLM | 10kV-500kV | |
| U210BM | 10kV-500kV | |
| U240BM | 10kV-500kV | |
Según la experiencia de Gaoya Power con más de 20 años en el suministro de aisladores de vidrio:
- Para líneas de transmisión de 220 kV, se recomiendan aisladores de vidrio con una resistencia mecánica de 160 kN o superior.
- Para líneas de ultra alta tensión (UAT) de 500 kV o más, normalmente se utilizan aisladores de vidrio con una resistencia mecánica de 300 kN o superior.
3. Consideraciones ambientales
Diferentes condiciones ambientales requieren distintos tipos de aisladores para un rendimiento óptimo:

- Aisladores de vidrio de perfil estándar: Adecuados para zonas con baja contaminación y condiciones ambientales convencionales.
- Aisladores de vidrio de perfil antipolución: Recomendados para áreas con niebla salina, alta humedad y alta contaminación, ya que cuentan con una mayor distancia de fuga para prevenir fallos relacionados con la contaminación.
- Aisladores de vidrio de perfil aerodinámico: Ideales para entornos áridos y arenosos, donde su diseño aerodinámico ayuda a reducir la acumulación de polvo y la adhesión de lluvia. También son adecuados para zonas desérticas y regiones con contaminación industrial.
- Aisladores de perfil estándar en climas fríos: En ambientes extremadamente fríos sin fuentes cercanas de contaminación, los aisladores de vidrio de perfil estándar son una opción apropiada.
¿Cómo afectan los contaminantes a los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión?
Contaminantes como el polvo, las emisiones industriales, la niebla salina y los excrementos de aves pueden debilitar el rendimiento de los aisladores de vidrio de varias maneras:
- Reducción del aislamiento y formación de capa conductora
La humedad convierte los contaminantes superficiales en una capa conductora, lo que incrementa la corriente de fuga y puede provocar descargas de arco o descargas disruptivas (flashover). - Riesgo de descarga por contaminación
En condiciones húmedas o con niebla, los contaminantes disminuyen la resistencia superficial, facilitando que la alta tensión provoque una ruptura del aire, generando cortocircuitos repentinos. - Aumento de la corriente de fuga y pérdida de energía
La presencia continua de una ruta conductora formada por contaminantes húmedos incrementa la corriente de fuga, lo que produce pérdida de energía, sobrecalentamiento y envejecimiento acelerado del aislador.
Cuatro soluciones para reducir los efectos de la contaminación en los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión
- Utilizar aisladores antipolución
Diseñados con largas distancias de fuga, estos aisladores aumentan el recorrido superficial de la corriente de fuga, reduciendo el riesgo de descargas disruptivas. - Realizar limpieza periódica
El lavado con agua a alta presión o la limpieza manual ayudan a eliminar los contaminantes acumulados y a mantener el rendimiento del aislamiento. - Aplicar recubrimientos antifouling
Recubrimientos como el caucho de silicona mejoran la hidrofobicidad, evitan la absorción de humedad y reducen el riesgo de flashover. - Optimizar la configuración del aislamiento
Aumentar el número de aisladores en la cadena mejora el nivel global de aislamiento, reduciendo el impacto de la contaminación ambiental.
¿Por qué elegir aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión?
- Alta resistencia mecánica y seguridad
Los aisladores de vidrio para alta tensión son tratados térmicamente (templados), lo que les otorga una excelente resistencia mecánica a la tracción. Pueden soportar con facilidad la tensión de la línea, siendo ideales para líneas de gran vano y zonas con fuertes vientos. Los productos estándar ofrecen una resistencia que va desde 40 kN hasta 300 kN, garantizando un amplio margen de seguridad. - Superficie lisa – Menor acumulación de polvo
La superficie del vidrio es muy lisa, lo que ayuda a evitar la acumulación de suciedad. Esto les permite un mejor desempeño que los aisladores de porcelana o polímero en entornos con contaminación media o alta, manteniendo un excelente aislamiento a lo largo del tiempo. - Autodestrucción visible – Fácil inspección y mantenimiento
En caso de falla o ruptura interna, el aislador de vidrio se fragmenta en pequeños trozos (proceso de autodestrucción), mientras que los herrajes metálicos permanecen conectados. Esto facilita a los técnicos detectar visualmente las unidades dañadas, agilizando la inspección y mejorando la eficiencia del mantenimiento. - Larga vida útil y bajo coste operativo
Los aisladores de vidrio presentan una gran resistencia al envejecimiento y al deterioro. A diferencia de los de porcelana, no sufren degradación del rendimiento eléctrico con el tiempo. Su vida útil supera normalmente los 30 años, con un mantenimiento mínimo, lo que se traduce en menores costes operativos a largo plazo. - Ecológicos y totalmente reciclables
El vidrio es un material inerte, no tóxico y 100% reciclable por la industria vidriera. Además, los componentes metálicos (como tapas, pernos y pasadores) también pueden reciclarse, y el cemento endurecido puede triturarse para utilizarse como árido reciclado (RCA) en aplicaciones de construcción.

